- 15455 NW Greenbrier Parkway, Suite 130 Beaverton, OR - 97006
- PH: (503) 376-9200
- FAX: (503) 376-9201
- info@cornellpainclinic.com
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP)
What is PRP ?
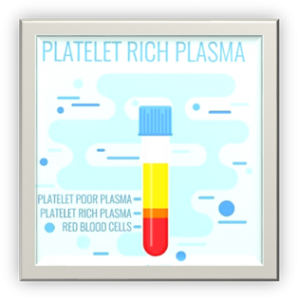
Although blood is mainly a liquid (called plasma), it also contains small solid components (red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.) The platelets are best known for their importance in clotting blood. However, platelets also contain hundreds of important growth factors which are very important in the healing from injuries.
PRP is plasma with many more platelets than what is typically found in blood. The concentration of platelets — and, thereby, the concentration of growth factors — can be 4 to 8 times greater (or richer) than usual.
To develop a PRP preparation, blood must first be drawn from a patient. The platelets are separated from other blood cells and their concentration is increased during a process called centrifugation.
Platelet rich plasma is a biological means of stimulating wound healing and tissue regeneration.
First developed in 1970s, it has been used over last 40 years to improve healing in dental, cosmetic, facial procedures and increasingly used over last decade for Orthopedic conditions and during surgeries.
Why platelets ?
Platelets are important component of our blood to aggregate and aiding blood clot formation after any injury. They also release more than 30 bioactive proteins( growth factors) that initiate hemostasis and regulate healing.
Platelet contains numerous growth factor proteins stored inside alpha granules like : –
Platelet derived growth factor (PGDF)
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
Epidermal growth factor (EGF)
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)
Transforming growth factor (TGF)
These growth factors released from platelets promote tissue healing in different phases by
1. Stimulating cell replication
2. Promote angiogenesis (blood vessel formation)
3. Promote tissue granulation formation( vascular tissue regrowth)
4. Promote growth of extracellular matrix( supporting tissue)
How does healing occur ?
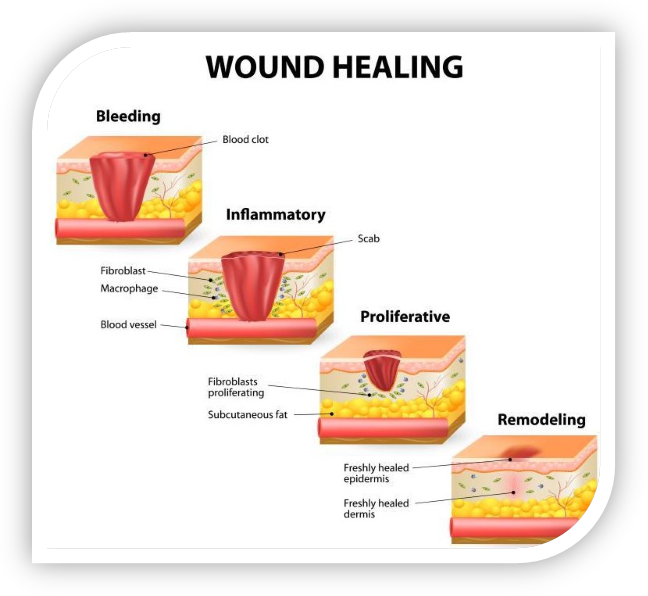
Regenerative therapy like PRP works by supportive or stimulating your natural healing mechanism, just like you experience after a injury. This healing occurs in 3 different phases
Phase 1: Inflammation: During which you may experience increase pain, and its important not to inhibit this phase of healing by steroids or Anti-inflammatory medications. Hence you are advised to stop taking Ibuprofen, Alleve which prevents this important part of our healing process.
Phase 2: Cell proliferation and matrix deposition: Tranforming growth factor( TGF) and many other growth factors stimulate cellular growth and deposition of stroma( supporting tissue)
Phase 3: Matrix Remodeling: Matrix metalloproteinases and other scavenger cells act as a cleaning crew and remove debris and excess of tissue during the healing process.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells: The ‘other’ bone marrow stem cells
You may hear the term “mesenchymal stem cell” or MSC to refer to cells isolated from stroma, the connective tissue that surrounds other tissues and organs. These cells are more accurately called “stromal cells” by many scientists.
The first MSCs were discovered in the bone marrow and were shown to be capable of making bone, cartilage and fat cells. Since then, they have been grown from other tissues, such as fat and cord blood.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can make several types of cells belonging to our skeletal tissues, such as cartilage, bone and fat. Scientists and practitioners have gathered enough evidence to use MSCs for treating bone and cartilage diseases.
Various MSCs are being tested and researched as treatments for a great many disorders, but there is little evidence to date that they are beneficial in diseases such as Autism, Parkinson’s, Macular degeneration and many other Neurodegenerative disorders.
Coming from different areas of body, Researchers believe that not all MSCs are the same, and that their characteristics depend on where in the body they come from and how they are isolated and grown.
What do we know?
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent stem cells found in bone marrow that are important for making and repairing skeletal tissues, such as cartilage, bone and the fat found in bone marrow. These are not to be confused with hematopoietic (blood) stem cells that are also found in bone marrow and make our blood.
MSCs make up a very small fraction of all the cells in our bone marrow, but through studies and research we have been able to isolate MSCs so they can be used for treatment for common orthopedic, spine and musculoskeletal conditions. MSCs are important for creating a niche environment or ‘home’ for blood stem cells in bone marrow.
Scientific Evidence for Mesenchymal Stem cell treatment?
Advances in scientific understanding of degenerative cellular and connective tissue process; lack of long-term efficacy of steroid injection therapies has prompted the need for alternative therapies.
PRP and Mesenchymal stem cell therapy have been used as both principal treatment and augmentative therapy alongside surgical repair.
Good quality evidence is still to come for many disorders. In Sports Medicine, Orthopedic and spine disorders; there is growing evidence for following conditions
TENDINOPATHIES
Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy
Achilles Tendinopathy
Patellar Tendinopathy
Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy
Plantar fascia Aponeurosis Pain
Greater Trochanteric Pain/ Gluteus Medius Tendinopathy
LIGAMENT
Anterior Cruciate Ligament( ACL of knee joint)
Ulner Collateral Ligament of the Elbow
CARTILAGE
Knee Osteoarthritis: Several study trials has shown promising results for Mild to Moderate Osteoarthritis.
Meniscus Injury( Knee): Few studies showing benefit of PRP or MSC therapy
INTERVERTEBRAL DISC
Few studies showing promising benefit to treat Discogenic low back pain