Have you been experiencing numbness or tingling in your back, arm or legs? Have you been experiencing sharp, shooting pain in your back, arms or legs? Do you have weakness of arm and leg muscles?
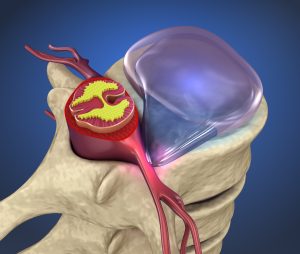
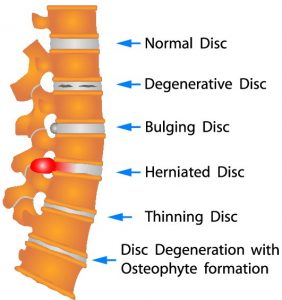
Hernaited disc in human spine in details
These are all classic symptoms and signs of herniated discs (disks), and should be evaluated as soon as possible by your doctor.
What is a Herniated or Slipped Disc?
Herniated disc is a medical condition affecting the spine in which soft inner portion of rubbery cushions (called the disks) leaks or bulge out in between two bones(vertebrae) of the spine.
Herniated discs (often called a slipped disk or ruptured disk) usually occur in the neck region (called the cervical spine), or in the lower back region (lumbar spine). However, herniated discs can occur anywhere along the spine.
Common Symptoms of Herniated or Slipped Discs
Symptoms of disc herniation varies from location of disc herniation and type of tissue involved. It can range from little or no pain to severe unrelenting neck or low back pain
Classic signs and symptoms of a herniated disc include:
- arm or leg pain
- numbness in the affected body part
- tingling in the affected body part
- weakness of the muscles
If you notice pain frequently spreading down your leg or arm, call your doctor right away. If this pain is accompanied by weakness, bowel or bladder symptoms, be sure to call your doctor right away.
What Causes Herniated or Slipped Discs?
Disk degeneration often leads to in disc herniation for some patients. The discs suffer wear and tear over time with natural daily stress and minor injuries, which leads to more disc bulging or protrusion and then more problematic disc herniation.
Other times, patients cannot pinpoint a specific cause of disc herniation. Any of the following causes may be possibilities, though:
- lifting or moving heavy loads—twisting or turning while lifting

- Professional athletes: especially those playing contact sports are prone to disc herniations
- a traumatic injury
- an excessive strain to the back
Risk factors that may increase the chances of a herniated risk:
- excess weight
- genetics: several genes are associated with Degenerative disc disease


 Arthritis is the most common cause of disability in United States, generally it is a progressive disease. When it becomes severe it can restrict your daily functional abilities. If arthritis affects your weight-bearing joints (Hips, knees, ankles, feet, etc.), patients can experience difficulty with walking and sitting up straight.
Arthritis is the most common cause of disability in United States, generally it is a progressive disease. When it becomes severe it can restrict your daily functional abilities. If arthritis affects your weight-bearing joints (Hips, knees, ankles, feet, etc.), patients can experience difficulty with walking and sitting up straight.






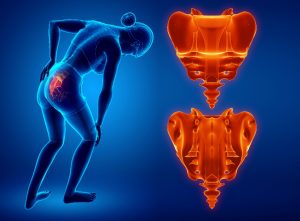





 Facet joint syndrome (also known as facet joint disease, facet osteoarthritis, facet hypertrophy or facet arthritis) is a syndrome in which facet joints degenerate to the point of causing painful symptoms.
Facet joint syndrome (also known as facet joint disease, facet osteoarthritis, facet hypertrophy or facet arthritis) is a syndrome in which facet joints degenerate to the point of causing painful symptoms.