Stellate Ganglion Block for PTSD.
Stellate ganglion block has shown promising results for treatment of PTSD symptoms by reducing dysfunctional sympathetic tone and reducing hyper-arousal and inability to relax
Introduction:
Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a chronic anxiety disorder caused by perceived or experiencing traumatic events. Sometimes things happen to people that are unusually frightening, horrible, or traumatic. For example:
- Military individuals exposed to War and close combat exercises
- A Severe accident or fire
- Seeing someone being killed or seriously injured
- An earthquake or flood
- Having a loved one die through suicide or homicide
- A Physical or Sexual assaults or abuse
Many cases of acute stress reaction naturally resolve by 1 year. Some individuals continue to experience Intrusive memories of traumatic events, leading to avoid trauma related activities, having negative thoughts and feeling leading to Persistent depression and anxiety. These individuals are diagnosed to have Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). PTSD often leads to prolonged debilitating symptoms and dysfunction.
Standard Treatment for PTSD:
Medications
Selective Serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Zoloft, Prozac, Paxil, Celexa, Lexapro etc
Serotonin Nor-epinephrine re-uptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Effexor, Cymbalta etc
Sympathetic blockers
- Prazosin for nightmares
- Clonidine for anxiety and sleep issues
Therapy
Exposure based Psychotherapy
- Cognitive processing therapy
- Trauma- focused psychotherapy
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy
- Virtual reality re-exposure therapy
Stress reduction strategies
- Meditation
- Yoga
Despite currently available treatments such as medications and Psychotherapy, around 50-70% individuals continue to struggle with PTSD symptoms and discontinue treatment before making enough progress in their treatment. Current challenges of standard treatment are:
- Slow onset of action of medications
- Medications effective for only 30-50% individuals
- Continued side effects of medications
- Need for prolonged patient involvement for Psychotherapy
Role of Sympathetic nervous system in PTSD:
The sympathetic nervous system is part of Autonomic nervous system, which on activation mobilizes our bodily resources for flight or fight response. It leads to increase in heart rate, alertness, arousal needed to tackle the acutely stressful situation.
Many research studies suggest that the continuous dysfunction of the sympathetic nervous system in PTSD causes prolonged arousal, hyper-vigilance, and aggravates PTSD related anxiety symptoms.
Stellate Ganglion block
Role of Stellate ganglion in our body
Stellate ganglion is a group of nerves at base of neck, which can be seen as command center from where sympathetic impulses reach to head, neck, arm and chest region. Blocking the stellate ganglion blocks the sympathetic nervous system, thus providing relief in neuropathic pain.
History of Stellate ganglion block use for PTSD
Stellate ganglion block(SGB) has been a routine procedure in Pain Medicine since early 1940s. It has been used to suppress sympathetic impulses and treat complex neurological disorders like complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS)
A study in 1990 reported that use of the Stellate Ganglion Block (SGB) technique lead to in the PTSD symptoms in patient experiencing both CRPS and PTSD.
This procedure was expressly used to treat for the first time in 2008. Since then, many studies, including multicenter randomized controlled trials have demonstrated an improvement in PTSD symptoms with the use of this therapy.
A Medscape Psychiatry news article discusses the use of Stellate ganglion block as an quick and effective treatment option for PTSD symptoms. An episode on the popular show 60 minutes talks about this procedure in detail
How does Stellate ganglion block help for PTSD?
Stellate Ganglion Block serves to regulate the sympathetic nervous system. This block is not a “cure” and symptoms may return with an incidental trigger. A patient is likely to benefit from repeat treatment if they have at least one documented positive response with this procedure.
During traumatic situations, our body naturally releases cortisol-stress hormone through activation of Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis and activating Sympathetic nervous system. These two regions in our brain- Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis and Autonomic nervous system are important mediators for PTSD related symptoms. Norepinephrine , a chemical released by the autonomic nervous system and found normally in the body has been found to be important for the continuation of PTSD symptoms.
It can be assumed that external cortisol injection obviates the need for HPA axis and Sympathetic nervous system activation during traumatic situation. Studies have shown that a cortisol injection within hours of trauma prevented development of future PTSD, supporting the hypothesis.
Stellate Ganglion Block “resets” the chronically active Sympathetic nervous system.
Mechanism of Action: Exact mechanism of how SGB helps PTSD symptoms is unknown, however following hypothesis has been proposed.
1st hypothesis:
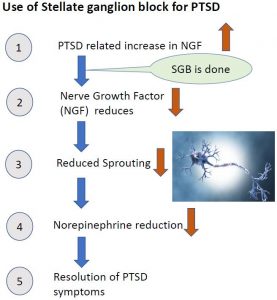
Stellate ganglion has a nervous system connection with Amygdala ( the brain center) which is activated in patients experiencing post traumatic stress disorder( PTSD). Stellate Ganglion reduces the nerve impulses and messages sent to the brain center thereby providing relief in the symptoms of PTSD .
2nd hypothesis:
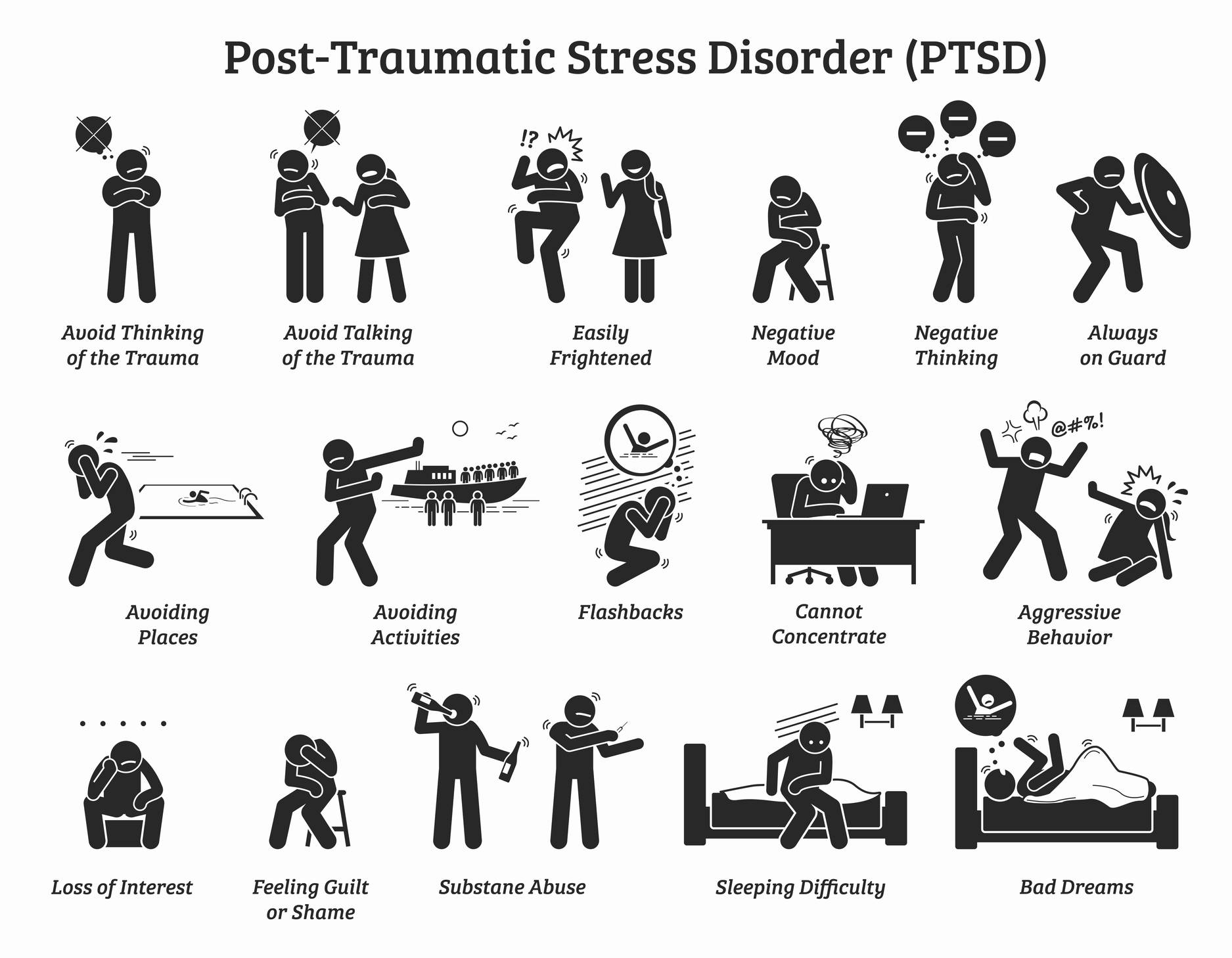
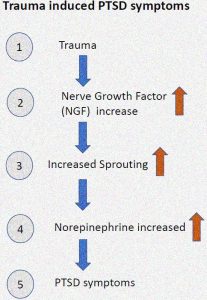
There is an increase in the Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) in PTSD patients which leads to an increase in the levels of Nor-epinephrine in the brain. This increase in the Nor-epinephrine levels exacerbates the symptoms of PTSD in patients. It is hypothesized that blocking the Stellate Ganglion, suppresses the Nerve Growth Factor, keeping the levels of Nor-epinephrine low and reversing the cascade of PTSD
Uses of Stellate ganglion block
Established uses: Neuropathic pain related to:
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS)
Post radiation neuritis
herpes Zoster
Post herpetic neuralgia
Neuropathic pain after limb ischemia (frost bite and Raynaud’s disease)
Potential uses: Some new indications
PTSD related anxiety disorder
Severe postmenopausal flushing
What to expect at a Procedure Visit?
After completing the legal paperwork, the medical assistant will check vitals and have the patient lie on their back on the X-ray table in the procedure room.
For a Right sided Stellate Ganglion block, patients are made to turn their neck slightly to their left side, and at this time a X-ray image is taken using a fluoroscopic machine.
The pain physician then performs a Fluoroscopic guided Stellate Ganglion block on the patient.
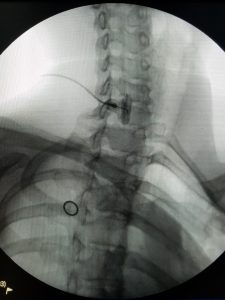
The patient will feel a tiny pinch (used for numbing the skin) and a small 2-inch needle is introduced through the skin up until it touches the side of the cervical spine (neck). A small amount (approx. 0.5 to 1cc) of contrast dye is injected to see the spread of dye inside the neck. Once the physician observes a safe and satisfactory spread of the dye, 7cc of local anesthetic (Bupivacaine or Ropivacaine) is injected in small increments to block the Stellate Ganglion
It is acceptable for the patient to talk during the injection. The patient should let the provider know if they have any new or strange sensations during the procedure, including tingling of the skin or mouth, ringing in the ears, or just feeling odd.
What to expect after the procedure?
Minor soreness around your neck is expected after the procedure.
Patient may also experience Horner’s syndrome temporarily after a successful Stellate Ganglion block. Some signs that one is experiencing Horner’s syndrome are
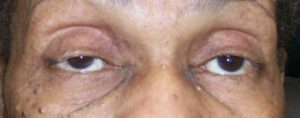
- constricted pupil (miosis),
- drooping of eyelid (ptosis),
- slight sinking in of eyeball – this is often hard to notice (enophthalmos),
- redness of the eye(scleral injection) and the
- absence of sweating on 1 half of face (anhidrosis)
Up to 15% cases also experience temporary hoarseness of voice or a sensation of something stuck on their back of the throat (Globus sensation). This happens due to spread of local anesthetic to nerves of larynx (voice box). This odd sensation or hoarseness of voice can last up to 8-10 hours.
Serious adverse effects like seizures, breathing difficulty or increasing pain in your neck due to Hematoma are very rare.
Follow up after Stellate ganglion block?
We recommend a close follow up at an interval of 7-10 days after the block to evaluate your response. At this time, your provider will discuss further course of action based on your body’s response to the procedure. The provider may recommend another round of procedure if the patient experienced Horner’s syndrome but insufficient relief of PTSD/ CRPS symptoms.
Are you a Candidate for Stellate ganglion block for PTSD?
The National center for PTSD consider 3 standardized scales for rating the severity of a patient’s PTSD symptoms
- Clinician administered PTSD Scale (CAPS): Administered by physician or provider
- PTSD checklist- Civilian version (PCL-Civilian): Self-administered
- PTSD Checklist- Military version (PCL- Military): Self-administered
A score of 32 or more on PTSD Checklist (PCL) indicates high likelihood of PTSD and treatment is deemed appropriate
You may be a candidate for Stellate ganglion block if you have been seeing a mental health provider and have tried medications for treatment of PTSD with inadequate relief. You may require an office consultation with your provider to establish you as a candidate for this procedure.
How likely you are going to get relief by Stellate ganglion block?
Each individual’s response to treatment varies. Currently research indicates that 70% individuals benefit from 1 or 2 stellate ganglion blocks administered within week of each other.
The onset of relief starts within an hour of the block and effect may last from weeks to months. You are more likely to notice the relief if your PTSD symptoms included hyper-vigilance, increased startle response, impaired concentration, insomnia – all signs of Sympathetic hypersensitivity that would decrease post procedure.
A Stellate Ganglion Block “resets” the chronically heightened inappropriate sympathetic nervous system activity. As described previously, this procedure is not a “cure” for PTSD, and symptoms may return with an incidental trigger. A positive response increases your chances of benefiting from repeat rounds of treatment.
Last but not the least, Stellate Ganglion block is not a stand-alone treatment. It is meant to facilitate psychotherapy and supplement the effects of psychotropic medications.
Is Stellate ganglion block safe?
To date, no long term complications have been reported as a result of Stellate Ganglion blocks.
In 1992, German researchers surveyed 45,000 completed Stellate Ganglion blocks and found the incidence of severe complications (such as seizures) to be only 1.7 in every 1000 patients. At the time, this procedure was being performed without the use of a fluoroscope or ultrasound machine and the complications were attributed to the spread of the anesthetic to the patient’s blood vessels.
The routine use of ultrasound or fluoroscopic guidance for this procedure nowadays has reduced the chances of complications even further.
Is Stellate ganglion block is covered by Insurances?
There are several studies over the last 10 years demonstrating the effectiveness of this procedure for treatment of PTSD. These studies primarily use data derived from active duty veterans in Veterans Affairs medical facilities. Researchers believe this procedure to be equivalent to SSRI antidepressant medications in their effect.
That being said, the body of evidence for the use of Stellate Ganglion block for treatment of PTSD is still emerging. Due to this, most insurance do not cover this procedure for the treatment of PTSD at this time. The scenario is similar to that of Ketamine use for treatment resistant depression which
was just approved in April 2019 even though it has been widely used by psychiatrists and anesthesiologists over the last 15 years.
How much Stellate Ganglion block costs ?
Cornell Pain Clinic has a unique advantage with our Clinic Director, Dr. Chand being dual trained in both Psychiatry and Anesthesia. Our mission is to deliver quality care to our patients by reducing the gap between mental health treatment and anesthesia based Interventional Pain procedures.
Please call our offices to set up consultation and get an out of pocket cost estimate for this procedure. Our team will work with your mental health and primary care providers to determine if Stellate Ganglion block is the best treatment option for you.
CONCLUSION: Stellate Ganglion block is emerging as an additional, fast acting, effective therapy for managing the symptoms of PTSD. It is an adjunct treatment that can supplement standard medications and psychotherapy to provide long lasting relief for patients suffering from Post Traumatic Stress Disorders.
REFERENCES:
Lipov E and Kelzenberg Briana. Sympathetic system modulation to treat post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): A review of clinical evidence and neurobiology. Journal of Affective Disorders 142 (2012) 1–5
Olmstead et al 2019. Effect of Stellate Ganglion Block Treatment on Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.3474
Summers MR and Nevin RL. Stellate Ganglion Block in the Treatment of Post-traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of Historical and Recent Literature. Pain Pract. 2017 Apr;17(4):546-553. doi: 10.1111/papr.12503. Epub 2016 Oct 14
Mulvaney et al. Stellate Ganglion Block Used to Treat Symptoms Associated With Combat-Related Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Case Series of 166 Patients. MILITARY MEDICINE, 179, 10:1133, 2014
Lipov et al. Stellate Ganglion Block Improves Refractory Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Associated Memory Dysfunction: A Case Report and Systematic Literature Review. MILITARY MEDICINE, 178, 2: e260, 2013
Lipov et al. Possible Reversal of PTSD-Related DNA Methylation by Sympathetic Blockade. J Mol Neurosci (2017) 62:67–72 DOI 10.1007/s12031-017-0911-3
Mulvaney et al. Clinical Guidelines for Stellate Ganglion Block to Treat Anxiety Associated With Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Journal of Special Operations Medicine Volume 15, Edition 2/Summer 2015
Lipov E and Ritchie EC. A Review of the Use of Stellate Ganglion Block in the Treatment of PTSD. Curr Psychiatry Rep (2015) 17:63 DOI 10.1007/s11920-015-0599-4
Leave a reply
I would like to receive information about SGB. for Ptsd. Do I need referral, is it covered by insurance. what is the process for treatment at your clinic.
ReplyWe don’t need referral for consultation appointment to discuss your symptoms and possible treatment. Currently most insurances are not covering SGB. for PTSD.
ReplyPlease call us@ 503-376-9200 at our office hours 8am-5pm for an appointment and any other information you may need.
Thanks, Dr. Suresh Chand
I have PTSD. I’d like more information. Cost etc.
ReplyHave bad anxiety due to tinnitus taking medication not helping
ReplyWondering if this may be another option
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and the military are commonly linked. PTSD can be considered a “young” diagnosis. It was not until 1980 that the diagnosis of PTSD as we know it today came to be. However, throughout history, people have recognized that exposure to combat situations can have a profound negative impact on the minds and bodies of those involved in these situations. In fact, the diagnosis of PTSD originates from observations of the effect of combat on soldiers. The grouping of symptoms that we now refer to as PTSD has previously been described in the past as “combat fatigue,” “shell shock,” or “war neurosis.” Furthermore, PTSD can also be acquired by anyone who has not seen combat or armed conflict depending on the stress factors.
ReplyI wish to to be considered for the SGB
Replytreatment, because I’m an ex-combat,
Ex-LEO, terrible abusive childhood,
I’ve been on 3/4 out of the 5 main anti- depressants over the past 20 + yrs.
I’m ready for the SGB treatment.
I am in NYC and interested in the procedure.
ReplyI never thought I would be herpes negative again after been diagnosed for 4 years, I have tried everything possible in life from one medical doctor to another, one hospital to another, series of tests, different kinds of medication, I had already lost hope until I meet Great Dr. Riaria online testimonies, a specialist in herbal medication from Africa, I contacted him through his email and number I got from one of the many testifiers, and he prepared herpes herbal medication for me which I took for weeks and now I am completely cured. I have gone to different hospitals for check ups to be totally sure, and all my results are negative. I want to use this medium to express my gratitude to him for saving my life and curing me from herpes virus, for taking away all my pains and sorrows, I’m indeed grateful and I am so happy I’m now herpes negative. I will continue to tell the good news of your great works to everyone, if you have herpes virus or other disease contact him now via: drriaria@gmail.com or WhatsApp him on +2349134987375.
Replyhttps://web.facebook.com/Dr-Riaria-Herbal-Home-102467701992890
Am tracy by name,from Germany, i was diagnosed with Herpes for 6years ago i lived in pain with the knowledge that i wasn’t going to ever be well again i contacted so many herbal doctors on this issue and wasted a large sum of money but my condition never got better i was determined to get my life back so one day i saw mrs neme amber post on how Dr Emmanuel saved him from the VIRUS with herbal medicine i contacted Dr Emmanuel on his email address: nativehealthclinic@gmail.com or WhatsApp +2348140073965 we spoke on the issue i told him all that i went through and he told me not to worry that everything will be fine again so he prepared the medicine and send it to me through courier service and told me how to use it,after 18days of usage I went to see the doctor for test ,then the result was negative,am the happiest woman on earth now. this testimony .is real.thanks to Dr Emmanuel God bless you…
ReplyHe also cured,Genital herpesGenital wattHIV/aidsCancerDiabetesHPVBrain tumorEx back love spellhttps://www.facebook.com/Dr_Emmanuel9-105748441179562/